

Glossary Box plot a graph that gives a quick picture of the middle 50% of the data First Quartile the value that is the median of the of the lower half of the ordered data set Frequency Polygon looks like a line graph but uses intervals to display ranges of large amounts of data Interval also called a class interval an interval represents a range of data and is used when displaying large data sets Paired Data Set two data sets that have a one to one relationship so that: Since 25% of values fall between 31 and 38, we know that fewer than 25% fall between 31 and 35. Twenty-five percent of the values fall in the interval 38 to 41, and 25% fall between 41 and 64.
What is a box and whisker plot used for series#

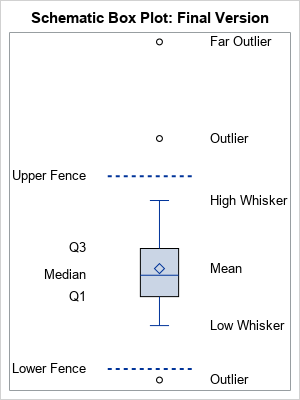
We use these values to compare how close other data values are to them. A box plot is constructed from five values: the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value. They also show how far the extreme values are from most of the data. Testing the Significance of the Correlation Coefficientīox plots (also called box-and-whisker plots or box-whisker plots) give a good graphical image of the concentration of the data. Hypothesis Testing for Two Means and Two Proportions Two Population Means with Known Standard DeviationsĬomparing Two Independent Population Proportions Two Population Means with Unknown Standard Deviations Hypothesis Testing of a Single Mean and Single Proportion
What is a box and whisker plot used for full#
Rare Events, the Sample, Decision and ConclusionĪdditional Information and Full Hypothesis Test Examples Outcomes and the Type I and Type II Errorsĭistribution Needed for Hypothesis Testing The Central Limit Theorem for Sample Means (Averages)Ī Single Population Mean using the Normal DistributionĪ Single Population Mean using the Student t Distribution Mean or Expected Value and Standard Deviationĭiscrete Distribution (Playing Card Experiment)ĭiscrete Distribution (Lucky Dice Experiment) Probability Distribution Function (PDF) for a Discrete Random Variable Independent and Mutually Exclusive Events Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Time Series Graphs Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots), Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs Definitions of Statistics, Probability, and Key Termsĭata, Sampling, and Variation in Data and Samplingįrequency, Frequency Tables, and Levels of Measurement


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
